GraphQL API Crawler
This guide will explain how to use the
graphql_factory
factory function to automatically introspect, build queries, and scrape GraphQL
APIs, including support for pagination and dependencies.
Defining Your GraphQL Resource
In this example, we will create a GraphQL asset that fetches transactions from
the
Open Collective API.
The API has a transactions query that returns a list of transactions.
The GraphQL factory will introspect the schema, generate queries, extract the relevant data, and return clean assets with minimal configuration.
1. Create the Configuration
The first step is to define a configuration object that describes your GraphQL resource. For the Open Collective transactions example, we set the endpoint URL, define query parameters, and specify a transformation function to extract the data we need.
from dagster import AssetExecutionContext
from ..factories.graphql import (
GraphQLResourceConfig,
PaginationConfig,
PaginationType,
RetryConfig,
graphql_factory,
)
from ..factories.dlt import dlt_factory
from ..config import DagsterConfig
# Configuration for the main transactions query
config = GraphQLResourceConfig(
name="transactions",
endpoint="https://api.opencollective.com/graphql/v2",
masked_endpoint="***",
target_type="Query",
target_query="transactions",
max_depth=2, # Limit the introspection depth
parameters={
"type": {
"type": "TransactionType!",
"value": "CREDIT",
},
"dateFrom": {
"type": "DateTime!",
"value": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
},
"dateTo": {
"type": "DateTime!",
"value": "2024-12-31T23:59:59Z",
},
},
pagination=PaginationConfig(
type=PaginationType.OFFSET,
page_size=100,
max_pages=5,
rate_limit_seconds=0.5,
offset_field="offset",
limit_field="limit",
total_count_path="totalCount",
),
exclude=["loggedInAccount", "me"], # Exclude unnecessary fields
transform_fn=lambda result: result["transactions"]["nodes"],
retry=RetryConfig(
max_retries=3,
initial_delay=2.0,
max_delay=30.0,
backoff_multiplier=2.0,
jitter=True,
reduce_page_size=True,
min_page_size=10,
page_size_reduction_factor=0.5,
),
)
For the full GraphQLResourceConfig spec, see the
source
In this configuration, we define the following fields:
- name: A unique identifier for the dagster asset.
- endpoint: The URL of the GraphQL API.
- masked_endpoint: The masked URL of the GraphQL API. If exists, it will be used for logging instead of the real endpoint.
- target_type: The GraphQL type containing the target query (usually "Query").
- target_query: The name of the query to execute.
- max_depth: The maximum depth of the introspection query. This will generate a query that explores all fields recursively up to this depth.
- parameters: A dictionary of query parameters. The keys are the parameter names, and the values are dictionaries with the parameter type and value.
- pagination: A configuration object that defines how to handle pagination. It includes the pagination type, page size, maximum number of pages to fetch, rate limit in seconds, and the fields used for offset and limit.
- exclude: A list of field names to exclude from the GraphQL schema expansion.
- transform_fn: A function that processes the raw GraphQL response and returns the desired data.
2. Build the Asset with Dependencies
The GraphQL factory now returns a dlt.resource directly and supports
dependency chaining. You can create assets that depend on the results of other
GraphQL queries:
def fetch_account_details(context: AssetExecutionContext, global_config: DagsterConfig, transaction_data):
"""
Dependency function that fetches account details for each transaction.
This function receives individual transaction items and yields account data.
"""
account_config = GraphQLResourceConfig(
name=f"account_{transaction_data['fromAccount']['id']}",
endpoint="https://api.opencollective.com/graphql/v2",
masked_endpoint="***",
target_type="Query",
target_query="account",
parameters={
"id": {
"type": "String",
"value": transaction_data["fromAccount"]["id"],
},
},
transform_fn=lambda result: result["account"],
max_depth=2,
exclude=["parentAccount", "stats"],
)
# The dependency yields data from the nested GraphQL query
yield from graphql_factory(account_config, global_config, context, max_table_nesting=0)
@dlt_factory(
key_prefix="open_collective",
)
def transactions_with_accounts(context: AssetExecutionContext, global_config: DagsterConfig):
"""
Main asset that fetches transactions and their associated account details.
"""
config = GraphQLResourceConfig(
name="transactions_with_accounts",
endpoint="https://api.opencollective.com/graphql/v2",
masked_endpoint="***",
target_type="Query",
target_query="transactions",
parameters={
"type": {"type": "TransactionType!", "value": "CREDIT"},
"dateFrom": {"type": "DateTime!", "value": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z"},
"dateTo": {"type": "DateTime!", "value": "2024-12-31T23:59:59Z"},
},
pagination=PaginationConfig(
type=PaginationType.OFFSET,
page_size=50,
max_pages=2,
rate_limit_seconds=1.0,
),
transform_fn=lambda result: result["transactions"]["nodes"],
max_depth=2,
exclude=["loggedInAccount", "me"],
deps=[fetch_account_details], # Dependencies to execute for each item
deps_rate_limit_seconds=1.0, # Rate limit between dependency calls
retry=RetryConfig(
max_retries=2,
initial_delay=1.0,
reduce_page_size=True,
min_page_size=5,
),
)
# Return the configured resource
yield graphql_factory(config, global_config, context, max_table_nesting=0)
The GraphQL factory function now takes a mandatory config argument,
global_config (DagsterConfig), and AssetExecutionContext. The
global_config is required for Redis caching functionality that stores GraphQL
introspection results for 24 hours, preventing overwhelming of external
services. Additional arguments are passed to the underlying dlt.resource
function, allowing you to customize the behavior of the asset.
For the full reference of the allowed arguments, check out the DLT
resource documentation.
3. Dependency System
The new dependency system allows you to:
- Chain GraphQL queries: Use results from one query to feed parameters into another
- Transform data flow: The main query results become intermediate data that feeds dependencies
- Return consistent shape: Only the dependency results are yielded to the final dataset
- Rate limit dependencies: Control the rate of dependent API calls
Tree-like Dependency Structure
Dependencies can be viewed as a tree structure where:
- The root is your main GraphQL query
- Branches are dependency functions that process each item from the parent
- Leaves are the final data shapes that get yielded to your dataset
Main Query (transactions)
├── Item 1 → fetch_account_details() → Account Data (leaf)
├── Item 2 → fetch_account_details() → Account Data (leaf)
└── Item 3 → fetch_account_details() → Account Data (leaf)
Data Shape Merging
When deps is provided, DLT automatically handles different data shapes:
- The main query executes and fetches data
- Each item from the main query is passed to dependency functions
- Dependency functions can execute additional GraphQL queries with different schemas
- DLT merges different data shapes from dependencies automatically
- Only leaf nodes (final dependency results) are included in the final output
- The main query data serves as intermediate processing data and is discarded
This means you can have dependencies that return completely different data structures (e.g., transactions → accounts → users), and DLT will intelligently combine them into a coherent dataset, only preserving the final leaf data from your dependency tree.
How to Run and View Results
If you have not setup your local Dagster environment yet, please follow our quickstart guide.
After having your Dagster instance running, follow the
Dagster setup guide to materialize the assets. Our example
assets are located under assets/open_collective/transactions.
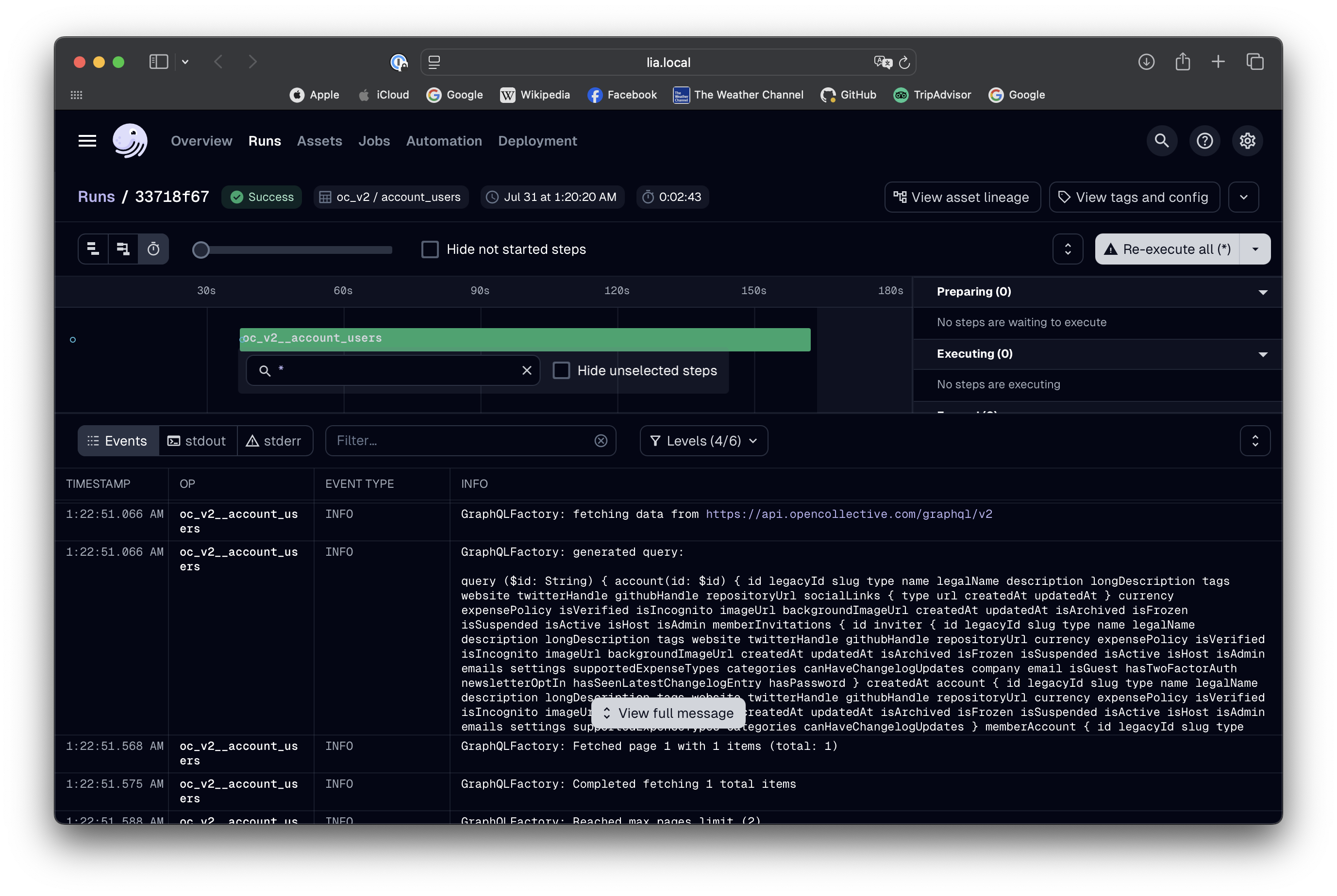
Running the pipeline will fetch the transactions from the Open Collective API following the configuration we defined. The factory will handle pagination automatically, fetching the data in chunks and combining them into a single result.
Advanced Features
Field Exclusion
Use the exclude parameter to skip unnecessary fields and reduce query
complexity:
config = GraphQLResourceConfig(
# ... other config
exclude=["loggedInAccount", "me", "stats.totalDonations"],
)
Custom Stop Conditions
Define custom conditions to stop pagination:
def stop_when_old_data(result, page_count):
# Stop if we encounter transactions older than 1 year
if result.get("transactions", {}).get("nodes"):
last_transaction = result["transactions"]["nodes"][-1]
transaction_date = last_transaction.get("createdAt")
# Add your date comparison logic here
return False # Continue pagination
return True # Stop pagination
pagination_config = PaginationConfig(
type=PaginationType.OFFSET,
stop_condition=stop_when_old_data,
# ... other pagination settings
)
Cursor-Based Pagination
For APIs that use cursor-based pagination:
pagination_config = PaginationConfig(
type=PaginationType.CURSOR,
page_size=50,
cursor_field="after",
page_size_field="first",
next_cursor_path="pageInfo.endCursor",
has_next_path="pageInfo.hasNextPage",
)
Keyset-Based Pagination
For APIs that use keyset-based pagination (also known as seek-based pagination):
pagination_config = PaginationConfig(
type=PaginationType.KEYSET,
page_size=100,
order_by_field="id",
order_direction="asc",
last_value_field="id_gt",
cursor_key="id",
page_size_field="first",
)
Error Handling and Retry Mechanism
The GraphQL factory includes a sophisticated retry mechanism with configurable debounce that helps handle transient failures and rate limiting:
from ..factories.graphql import RetryConfig
retry_config = RetryConfig(
max_retries=3, # Maximum number of retry attempts
initial_delay=2.0, # Initial delay in seconds before first retry
max_delay=30.0, # Maximum delay between retries
backoff_multiplier=2.0, # Multiplier for exponential backoff
jitter=True, # Add random jitter to delays
reduce_page_size=True, # Enable adaptive page size reduction
min_page_size=10, # Minimum page size when reducing
page_size_reduction_factor=0.5, # Factor to reduce page size by (50%)
continue_on_failure=True, # Log failures and continue instead of raising
)
config = GraphQLResourceConfig(
# ... other configuration
retry=retry_config,
)
Adaptive Page Size Reduction
When reduce_page_size=True, the retry mechanism implements intelligent
debounce behavior:
- Initial Query: Starts with configured page size (e.g., 50 items)
- First Failure: Waits 2 seconds, reduces to 25 items, retries
- Second Failure: Waits 4 seconds, reduces to 12 items, retries
- Third Failure: Waits 8 seconds, uses minimum 10 items, final retry
Key Benefits:
- Temporary Reduction: Page size reductions only apply to the current page's retry attempts
- Automatic Reset: After success, the next page returns to the original page size
- Progressive Backoff: More time waiting + fewer items = less aggressive on failures
- Rate Limit Friendly: Helps avoid overwhelming APIs during issues
Example Behavior
Page 1: Start with 50 items
[FAIL] Fails → retry with 25 items
[FAIL] Fails → retry with 12 items
[SUCCESS] Succeeds with 12 items
Page 2: RESETS to 50 items (not stuck at 12!)
[SUCCESS] Succeeds immediately with 50 items
Page 3: Start with 50 items again
[SUCCESS] Succeeds immediately with 50 items
Retry Configuration Options
- max_retries: Number of attempts before giving up
- initial_delay: Base delay before first retry (seconds)
- max_delay: Cap on delay duration to prevent excessive waits
- backoff_multiplier: How aggressively delays increase (2.0 = double each time)
- jitter: Adds randomness to prevent thundering herd effects
- reduce_page_size: Enable smart page size reduction on failures
- min_page_size: Prevent page sizes from getting too small
- page_size_reduction_factor: How much to reduce page size (0.5 = 50% reduction)
- continue_on_failure: Log failures and continue execution instead of raising exceptions when all retries are exhausted. Useful for APIs with broken entries or when certain queries consistently timeout due to heavy backend operations, allowing the run to complete by skipping problematic sections
Conclusion
The GraphQL factory provides a powerful way to create reusable assets that fetch data from GraphQL APIs with minimal configuration. The new version offers enhanced capabilities:
- Direct DLT integration: Returns
dlt.resourceobjects directly - Dependency chaining: Chain multiple GraphQL queries together
- Field exclusion: Skip unnecessary fields to optimize queries
- Smart retry mechanism: Configurable retry with adaptive page size reduction
- Enhanced error handling: Better logging and error reporting
- Flexible pagination: Support for offset, cursor, relay, and keyset-style pagination
This allows you to focus on the data you need and the transformations you want to apply, rather than the mechanics of constructing queries and managing API interactions.